Highlights
|
The Sun is a dynamic and active star, constantly churning with magnetic activity. This activity can sometimes erupt in powerful solar flares, which can send a torrent of energy and radiation hurtling towards Earth. In an 11-year solar cycle, there can be as many as 2,000 solar flares of varying strength. Not all of these flares will produce coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and in the vast expanse of space, fewer of those will hit Earth.
On August 7, 2023, the Sun unleashed a powerful solar flare that reached its peak at 4:46 p.m. EDT. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, a vigilant monitor of the Sun’s activities, captured the imagery.
The Sun emitted a strong solar flare on Aug. 7, 2023, peaking at 4:46 pm EDT. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured an image of the event, which was classified as X1.5. https://t.co/MEYYmrSDkI pic.twitter.com/0WCotB48eR
The solar flare was classified as an X1.5, which is the second-most powerful type of solar flare. The flare was so powerful that it caused a radio blackout event on the daylit side of the Earth. This means that radio communications were disrupted in most of the United States, Canada, and the Pacific Ocean.
The flare also caused minor disruption to GPS and satellite communications. However, there were no reports of any major damage or injuries caused by the flare.
This solar flare is a reminder of the power of the Sun and the potential impact that solar activity can have on Earth. In addition to the radio blackout, the X1.5 flare also caused a number of other effects on Earth.
The Sun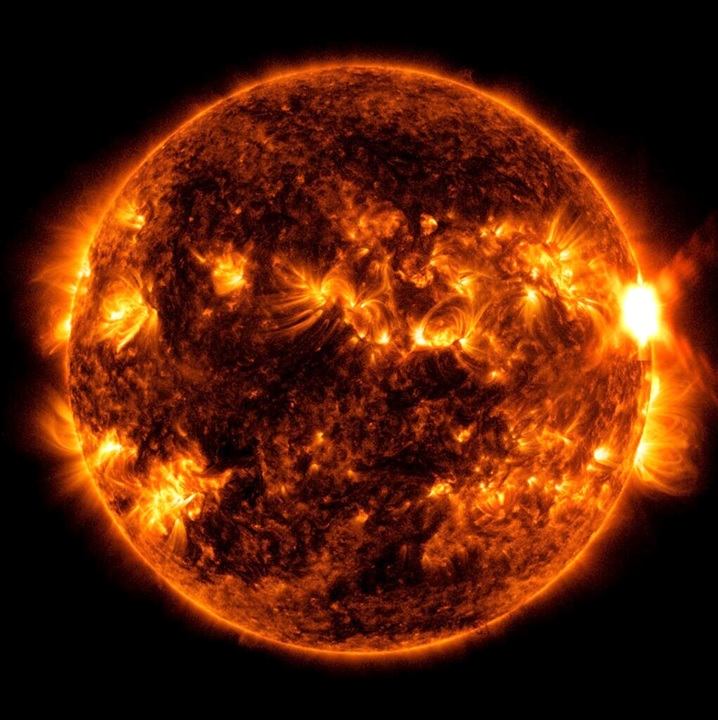 The Sun is a hot, glowing ball of hydrogen and helium at the centre of our solar system. It is about 4.5 billion years old and is the largest object in our solar system. The Sun's gravity holds the solar system together, keeping everything from the biggest planets to the smallest bits of debris in orbit around it. The Sun's core is the hottest part, with temperatures reaching up to 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius). The Sun's surface called the photosphere, is much cooler, at about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit (5,500 degrees Celsius). The Sun's outer atmosphere, the corona, is even hotter than the core, reaching up to 3.5 million degrees Fahrenheit (2 million degrees Celsius). |
What is a solar flare?

Image: NASA
A solar flare is a sudden, intense eruption of electromagnetic radiation from the Sun. Flares occur in active regions on the Sun, where intense magnetic fields are concentrated. When these magnetic fields become tangled and unstable, they can release a burst of energy that travels through the Sun's atmosphere and into space.
Also read: How long can humans live?
How does a solar flare occur?
Solar flares occur when the Sun's magnetic field becomes tangled and unstable. This can happen when sunspots, which are areas of intense magnetic activity, collide. When the magnetic fields of two sunspots collide, they can become twisted and knotted together. This can create a build-up of energy that is eventually released in a solar flare.
The Sun is making a splash this weekend. 🌊 ☀️
This solar flare, joined by a coronal mass ejection and filament eruption, was seen on the Sun on July 28.
Learn more about these explosive features: https://t.co/FhUDx7K1ci pic.twitter.com/EAkddTciIq — NASA Sun & Space (@NASASun) July 28, 2023
What are the different types of solar flares?
Solar flares are classified according to their strength, which is measured by the peak flux of soft X-rays emitted by the flare. The soft X-rays are emitted by the hot plasma that is accelerated during the flare.
The different types of solar flares are:
A-class flares: The weakest type of solar flare. A-class flares have a peak flux of 10^-8 to 10^-7 watts per square meter. They are not usually noticeable on Earth, but they can sometimes cause minor disruptions to radio communications.
B-class flares: Moderately strong solar flares. B-class flares have a peak flux of 10^-6 to 10^-5 watts per square meter. They can cause temporary radio blackouts and can sometimes disrupt GPS signals.
C-class flares: Strong solar flares. C-class flares have a peak flux of 10^-4 to 10^-3 watts per square meter. They can cause widespread radio blackouts and can sometimes damage satellites.
M-class flares: Very strong solar flares. M-class flares have a peak flux of 10^-2 to 10^-1 watts per square meter. They can damage satellites and disrupt power grids.
X-class flares: The most powerful type of solar flare. X-class flares have a peak flux of 10^0 to 10^1 watts per square meter. They can cause major disruptions to power grids, communication networks, and GPS systems.
In addition to these five main types of solar flares, there are also a few rarer types of flares, such as:
Gamma-ray solar flares: These are the most powerful type of solar flare. They emit gamma rays, which are the highest-energy form of electromagnetic radiation. Gamma-ray solar flares are extremely rare, and they have only been observed a handful of times.
Proton solar flares: These flares emit a large number of protons, which are positively charged particles. Proton solar flares can damage satellites and can also pose a health risk to astronauts in space.
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs): CMEs are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun. CMEs can cause geomagnetic storms on Earth, which can disrupt power grids and communication networks.
How does a solar flare affect Earth?
Solar flares can affect Earth in a number of ways. The most immediate effect is the release of high-energy particles into space. These particles can interact with Earth's atmosphere, causing auroras, or Northern Lights. They can also damage satellites and disrupt communication networks.
Do solar flares affect us on Earth? How often do they happen? Can we predict them?
Find the answers to these burning questions and more in the Solar Flares FAQs: https://t.co/h7qs65v8fb pic.twitter.com/uWM4vpkrKv — NASA Sun & Space (@NASASun) June 30, 2023
In addition to the direct effects of solar flares, they can also indirectly affect Earth by causing geomagnetic storms. Geomagnetic storms are caused by the interaction of solar wind with Earth's magnetic field. They can cause power outages, disruptions to communication networks, and damage to satellites.
The effects of solar flares on Earth can vary depending on the strength of the flare. Weak flares may have only minor effects, while strong flares can cause significant damage.
The August 7, 2023 solar flare was an X1.5 flare, which is the second-most powerful type of solar flare. This flare caused a radio blackout event on the daylit side of the Earth and may have damaged some satellites. However, there were no reports of any major damage or injuries caused by the flare.
Also read: EXPLAINED: Could Two Planets Be Sharing The Same Orbit Around A Star?
Also read: Europe Heatwave: What is it and what is causing it?
Also Read: What is a Black Hole? Which Is The Biggest Black Hole In The Universe?
