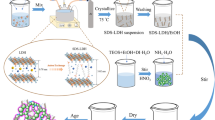
Abstract
Hydrophobic silica aerogel composite materials are considered as one of the most promising thermal insulation materials in energy-saving buildings. With the increasing negative effect on the environment of construction waste, it is necessary to develop an effectively recyclable thermal aerogel material for the building industry. In this work, we firstly employed a reversible gelling of hydrophobic silica aerogel microparticles dispersed with methyl cellulose surfactant (MCS) to prepare recyclable thermo-insulating panels (RTIP). The RTIP, with low bulk density (<0.05 g/m3) and thermal conductivity (0.027 W/(mK) at 20 °C), has a splintering mass loss of the composite material as low as 1% after 2 h continuous high-frequency oscillation, which was attributed to the rigid support of gelatinized MCS layers. Through mechanical mixing to re-dissolving in water, the reproducible RTIP can be obtained by the same gelling and drying process, with fairly stable hydrophobicity and thermal conductivity after 10 cycles. The strategy demonstrated here provides a new paradigm for developing environmentally-friendly materials for thermal-insulating buildings.

Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
A simple strategy was developed to prepare a highly uniform and stable hydrophobic silica aerogel aqueous solution.
-
Recyclable thermo-insulating panels exhibits high porosity, good mechanical strength, and low thermal conductivity (0.027 W/(mK) at 20 °C).
-
Recyclable thermo-insulating panels shows no obvious change in mechanical properties and thermal conductivity after five recyclable cycles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peter SC (2018) Reduction of CO2 to chemicals and fuels: a solution to global warming and energy crisis. Acs Energy Lett 3(7):1557–1561
Minas C, Carpenter J, Freitag J, Landrou G, Tervoort E, Habert G, Studart AR (2019) Foaming of recyclable clays into energy-efficient low-cost thermal insulators. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng 7(18):15597–15606
Hasper W, Kirtschig T, Siddall M, Johnston D, Vallentin G, Harvie-Clark J (2020) Long-term performance of Passive House buildings. Energy Effic 14(1):1–17
Ruparathna R, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2017) Rethinking investment planning and optimizing net zero emission buildings. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 19(6):1711–1724
Ramli Sulong NH, Mustapa SAS, Abdul Rashid MK (2019) Application of expanded polystyrene (EPS) in buildings and constructions: a review. J of Appl Polym Sci 136(20):47529
Pierre AC, Pajonk GM (2002) Chemistry of aerogels and their applications. Chem Rev 102(11):4243–4265
Reim M, Reichenauer G, Korner W, Manara J, Arduini-Schuster M, Korder S, Beck A, Fricke J (2004) Silica-aerogel granulate - Structural, optical and thermal properties. J Non-Cryst Solids 350:358–363
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi MH (2008) Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Tech 199(1-3):10–26
Zeng SQ, Hunt AJ, Cao W, Greif R (1994) Pore-size distribution and apparent gas thermal-conductivity of silica aerogel. J Heat Trans-T Asme 116(3):756–759
Gurav JL, Jung IK, Park HH, Kang ES, Nadargi DY (2010) Silica aerogel: synthesis and applications. J Nanomater 2010:409310. Artn
Berkefeld A, Heyer M, Milow B (2017) Silica aerogel paper honeycomb composites for thermal insulations. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol 84(3):486–495
Chang KJ, Wang YZ, Peng KC, Tsai HS, Chen JR, Huang CT, Ho KS, Lien WF (2014) Preparation of silica aerogel/polyurethane composites for the application of thermal insulation. J Polym Res 21(1):1–9
Ding JJ, Liu Q, Zhang B, Ye F, Gao Y (2020) Preparation and characterization of hollow glass microsphere ceramics and silica aerogel/hollow glass microsphere ceramics having low density and low thermal conductivity. J Alloy Compd 831:154737
Eskandari N, Motahari S, Atoufi Z, Motlagh GH, Najafi M (2017) Thermal, mechanical, and acoustic properties of silica-aerogel/UPVC composites. J of Appl Polym Sci 134(14):44685
Fricke J, Caps R, Buttner D, Heinemann U, Hummer E (1987) Silica aerogel - a light-transmitting thermal superinsulator. J Non-Cryst Solids 95(6):1167–1174
Gunay AA, Kim H, Nagarajan N, Lopez M, Kantharaj R, Alsaati A, Marconnet A, Lenert A, Miljkovic N (2018) Optically transparent thermally insulating silica aerogels for solar thermal insulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(15):12603–12611
Parmenter KE, Milstein F (1998) Mechanical properties of silica aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids 223(3):179–189
Li GA, Zhu TL, Ye LY, Deng ZX, Zhang YJ, Jiao F, Zheng HR (2009) Hydrophobic silica aerogel prepared in-situ by ambient pressure drying and its thermal stability. Acta Phys-Chim Sin 25(9):1811–1815
Shafi S, Zhao Y (2019) Superhydrophobic, enhanced strength and thermal insulation silica aerogel/glass fiber felt based on methyltrimethoxysilane precursor and silica gel impregnation. J. Porous Mater 27(2):495–502
Ul Haq E, Zaidi SFA, Zubair M, Karim MRA, Padmanabhan SK, Licciulli A (2017) Hydrophobic silica aerogel glass-fibre composite with higher strength and thermal insulation based on methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) precursor. Energ Buildings 151:494–500
Ge DT, Yang LL, Li Y, Zhao JP (2009) Hydrophobic and thermal insulation properties of silica aerogel/epoxy composite. J Non-Cryst Solids 355(52-54):2610–2615
Kim HM, Noh YJ, Yu J, Kim SY, Youn JR (2015) Silica aerogel/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) insulation composites with preserved aerogel pores using interfaces between the superhydrophobic aerogel and hydrophilic PVA solution. Compos Part a-Appl S 75:39–45
Zhang ZH, Shen J, Ni XY, Wu GM, Zhou B, Yang MX, Gu XH, Qian MJ, Wu YH (2006) Hydrophobic silica aerogels strengthened with nonwoven fibers. J Macromol Sci A 43(11):1663–1670
Madyan OA, Fan MZ (2018) Hydrophobic clay aerogel composites through the implantation of environmentally friendly water-repellent agents. Macromolecules 51(24):10113–10120
Mohammadi A, Moghaddas J (2015) Synthesis, adsorption and regeneration of nanoporous silica aerogel and silica aerogel-activated carbon composites. Chem Eng Res Des 94:475–484
Liu RY, Wang J, Du Y, Liao JH, Zhang XT (2019) Phase-separation induced synthesis of superhydrophobic silica aerogel powders and granules. J Solid State Chem 279:120971
Wang J, Zhang YL, Wei Y, Zhang XT (2015) Fast and one-pot synthesis of silica aerogels via a quasi-solvent-exchange-free ambient pressure drying process. Micropor Mesopor Mat 218:192–198
Wang J, Zhang YL, Zhang XT (2016) Reversible superhydrophobic coatings on lifeless and biotic surfaces via dry-painting of aerogel microparticles. J Mater Chem A 4(29):11408–11415
Xian AP (2000) Thermodynamic discussion on Young’s equation in wetting. Z Metallkd 91(4):316–322
Yamaguchi Y, Kusudo H, Surblys D, Omori T, Kikugawa G (2019) Interpretation of Young’s equation for a liquid droplet on a flat and smooth solid surface: Mechanical and thermodynamic routes with a simple Lennard-Jones liquid. J Chem Phys 150(4):044701
Wei PL, Hou K, Chen T, Chen GY, Mugaanire IT, Zhu MF (2020) Reactive spinning to achieve nanocomposite gel fibers: from monomer to fiber dynamically with enhanced anisotropy. Mater Horiz 7(3):811–819
Kundu PP, Kundu M, Sinha M, Choe S, Chattopadhayay D (2003) Effect of alcoholic, glycolic, and polyester resin additives on the gelation of dilute solution (1%) of methylcellulose. Carbohydr. Polym 51(1):57–61
Zhuo L, Ma C, Xie F, Chen S, Lu Z (2020) Methylcellulose strengthened polyimide aerogels with excellent oil/water separation performance. Cellulose 27(13):7677–7689
Jung HNR, Lee YK, Parale VG, Cho HH, Mahadik DB, Park HH (2017) Hydrophobic silica composite aerogels using poly(methyl methacrylate) by rapid supercritical extraction process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol 83(3):692–697
He S, Huang YJ, Chen GN, Feng MM, Dai HM, Yuan BH, Chen XF (2019) Effect of heat treatment on hydrophobic silica aerogel. J Hazard Mater 362:294–302
Al Zaidi IK, Demirel B, Atis CD, Akkurt F (2020) Investigation of mechanical and thermal properties of nano SiO2/hydrophobic silica aerogel co-doped concrete with thermal insulation properties. Struct. Concr 21(3):1123–1133
Li H, Xie ZL, Liu LL, Peng ZR, Ding QS, Ren LL, Ai D, Reainthippayasakul W, Huang YQ, Wang Q (2019) High-Performance Insulation Materials from Poly(ether imide)/Boron Nitride Nanosheets with Enhanced DC Breakdown Strength and Thermal Stability. Ieee T Dielect El In 26(3):730–737
Wong JCH, Kaymak H, Tingaut P, Brunner S, Koebel MM (2015) Mechanical and thermal properties of nanofibrillated cellulose reinforced silica aerogel composites. Micropor Mesopor Mat 217:150–158
Li Z, Gong LL, Cheng XD, He S, Li CC, Zhang HP (2016) Flexible silica aerogel composites strengthened with aramid fibers and their thermal behavior. Mater Design 99:349–355
Maleki H, Duraes L, Portugal A (2014) Synthesis of lightweight polymer-reinforced silica aerogels with improved mechanical and thermal insulation properties for space applications. Micropor Mesopor Mat 197:116–129
Binici H, Eken M, Kara M, Dolaz M (2014) An environment-friendly thermal insulation material from sunflower stalk, textile waste and stubble fibers. Constr Build Mater 51:24–33
Abu-Jdayil B, Mourad AH, Hittini W, Hassan M, Hameedi S (2019) Traditional, state-of-the-art and renewable thermal building insulation materials: an overview. Constr Build Mater 214:709–735
Cekon M, Struhala K, Slavik R (2017) Cardboard-based packaging materials as renewable thermal insulation of buildings: thermal and life-cycle performance. J Renew Mater 5:84–93
Jiri Z, Jitka H, Petranek V, Kosikova J, Korjenic A (2011) Investigation of thermal insulation materials based on easy renewable row materials from agriculture. advanced materials and structures. Pts 1 and 2 335-336:1412–1417
Rabold A, Hessinger J, Bacher S (2015) Thermal insulation composite system and outer insulations from renewable raw materials in the renovation of old buildings sound engineering design of exterior components in the rehabilitation. Bauphysik 37(1):57–61
Viel M, Collet F, Lanos C (2019) Development and characterization of thermal insulation materials from renewable resources. Constr Build Mater 214:685–697
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0203301, 2020YFB1505703), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52173052), and the Royal Society Newton Advanced Fellowship (NA170184).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Li, T., Wang, Z. et al. Recyclable thermo-insulating panels made by reversible gelling of dispersed silica aerogel microparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 106, 432–443 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05741-z